 |
| September 18, 2012 | Volume 08 Issue 35 |
Materials News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Weird stuff: Moon dust simulant for 3D printing
 Crafted from a lunar regolith simulant, Basalt Moon Dust Filamet™ (not a typo) available from The Virtual Foundry closely mirrors the makeup of lunar regolith found in mare regions of the Moon. It enables users with standard fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printers to print with unparalleled realism. Try out your ideas before you go for that big space contract, or help your kid get an A on that special science project.
Crafted from a lunar regolith simulant, Basalt Moon Dust Filamet™ (not a typo) available from The Virtual Foundry closely mirrors the makeup of lunar regolith found in mare regions of the Moon. It enables users with standard fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printers to print with unparalleled realism. Try out your ideas before you go for that big space contract, or help your kid get an A on that special science project.
Learn more.
Make nylon 3D-printed prototypes and parts in the office
 The new SLS 300 from 3D Systems is an affordable, turnkey, closed-loop 3D-printing system designed to operate in a smaller-footprint environment. SLS 300 makes selective laser sintering available to a broader range of customers with a high-reliability, affordable solution to produce end-use parts. Users can produce tough, durable parts from a range of production-grade nylon materials. Amazing fill, finishing, and clean-up systems.
The new SLS 300 from 3D Systems is an affordable, turnkey, closed-loop 3D-printing system designed to operate in a smaller-footprint environment. SLS 300 makes selective laser sintering available to a broader range of customers with a high-reliability, affordable solution to produce end-use parts. Users can produce tough, durable parts from a range of production-grade nylon materials. Amazing fill, finishing, and clean-up systems.
Learn more.
Will it erode? 3D-printing materials comparison from Xometry
 Which 3D-printed plastics are the toughest? In this "Will it ..." video, Greg Paulsen, Xometry's Director of Application Engineering, 3D printed Benchies (3D test models) using different materials (such as polycarbonate, PLA, polypropylene, ULTEM, and Nylon 11 and 12) and processes (such as FDM, SLS, MJF, SLA, LSPc, Polyjet, and DLS) and then ran several abrasion tests on them. Watch to find out which 3D-printed plastic is truly the toughest of them all!
Which 3D-printed plastics are the toughest? In this "Will it ..." video, Greg Paulsen, Xometry's Director of Application Engineering, 3D printed Benchies (3D test models) using different materials (such as polycarbonate, PLA, polypropylene, ULTEM, and Nylon 11 and 12) and processes (such as FDM, SLS, MJF, SLA, LSPc, Polyjet, and DLS) and then ran several abrasion tests on them. Watch to find out which 3D-printed plastic is truly the toughest of them all!
View Part 1.
View Part 2.
Graphene Handbook: Learn all about this wonder material
 Metalgrass LTD has published the 11th edition of its "Graphene Handbook," a comprehensive resource on graphene technology, the industry, and the market for this wonder material made of single layers of atoms of pure carbon. The book includes development history, production methods, current research, an intro to metrology and standardization, and even an investment guide. Under 100 bucks for digital edition. Hard copy available too.
Metalgrass LTD has published the 11th edition of its "Graphene Handbook," a comprehensive resource on graphene technology, the industry, and the market for this wonder material made of single layers of atoms of pure carbon. The book includes development history, production methods, current research, an intro to metrology and standardization, and even an investment guide. Under 100 bucks for digital edition. Hard copy available too.
Learn more.
Who knew? How colorants affect plastic
 In plastic injection molding, one aspect of polymer characteristics that doesn't always get the consideration it deserves is the addition of colorant. Believe it or not, there is a whole scientific body of knowledge about the ways in which adding color to plastic can affect its behavioral properties. This short article by Denny Scher of ICO Mold takes a high-level look at some of the different, and surprising, ways colorants can affect plastics.
In plastic injection molding, one aspect of polymer characteristics that doesn't always get the consideration it deserves is the addition of colorant. Believe it or not, there is a whole scientific body of knowledge about the ways in which adding color to plastic can affect its behavioral properties. This short article by Denny Scher of ICO Mold takes a high-level look at some of the different, and surprising, ways colorants can affect plastics.
Read the full article.
Retaining magnets from JW Winco: Universal and clever
 JW Winco has expanded its magnet line to support more applications with new materials, shapes, systems, and even raw magnets. Learn about their latest offerings, including retaining magnets designed for corrosive environments (GN 50.8), encapsulated magnets designed for sensitive or painted surfaces (GN 51.8), handle magnets (GN 53.3), and powerful magnets designed to handle challenging environs (GN 52.6).
JW Winco has expanded its magnet line to support more applications with new materials, shapes, systems, and even raw magnets. Learn about their latest offerings, including retaining magnets designed for corrosive environments (GN 50.8), encapsulated magnets designed for sensitive or painted surfaces (GN 51.8), handle magnets (GN 53.3), and powerful magnets designed to handle challenging environs (GN 52.6).
Learn more.
3D print tool steel with the ease of a plastic
 The Virtual Foundry, a pioneer in advanced 3D-printing materials, is excited to announce the launch of their latest innovation: M300 Tool Steel Filamet™ (not a typo). This material answers the demand for FFF 3D-printable Tool Steel, delivering unparalleled strength and versatility. What sets this material apart is its seamless compatibility with various 3D printers, including Creality, Bambu Lab, Ultimaker, and more. The filament prints effortlessly, resembling the ease of working with PLA (plastic).
The Virtual Foundry, a pioneer in advanced 3D-printing materials, is excited to announce the launch of their latest innovation: M300 Tool Steel Filamet™ (not a typo). This material answers the demand for FFF 3D-printable Tool Steel, delivering unparalleled strength and versatility. What sets this material apart is its seamless compatibility with various 3D printers, including Creality, Bambu Lab, Ultimaker, and more. The filament prints effortlessly, resembling the ease of working with PLA (plastic).
Learn more.
Great Resources: Sheet metal design guide
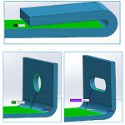 If you're looking for a basic guide to sheet metal design, this one from Xometry will serve your needs well. Follow the design requirements and tolerances in this guide to ensure parts fall closer to design intent. This is the type of information you'll sock away and then refer to again and again.
If you're looking for a basic guide to sheet metal design, this one from Xometry will serve your needs well. Follow the design requirements and tolerances in this guide to ensure parts fall closer to design intent. This is the type of information you'll sock away and then refer to again and again.
Read the full article.
Particle foam perfectly distributed thanks to simulation with Ultrasim
 BASF's Ultrasim simulation solution now includes Infinergy, an expanded thermoplastic polyurethane (E-TPU) that is used in a wide range of applications to make components with particle foam -- from bicycle tires to the soles on shoes. Identify and solve problems related to pneumatic filling when distributing particle foams in molds, even taking gravity and mold closing into consideration. Avoid those pesky air pockets.
BASF's Ultrasim simulation solution now includes Infinergy, an expanded thermoplastic polyurethane (E-TPU) that is used in a wide range of applications to make components with particle foam -- from bicycle tires to the soles on shoes. Identify and solve problems related to pneumatic filling when distributing particle foams in molds, even taking gravity and mold closing into consideration. Avoid those pesky air pockets.
Learn more.
Premium polymer DLP printer is half the price of its predecessor
 Desktop Metal has just launched the ETEC Pro XL -- a premium polymer digital light processing (DLP) printer that enters the market at less than half the price as its predecessor. DLP is regarded by many as a superior polymer 3D-printing technology for speed, surface finish, and accuracy. Ideal for automotive and machine parts, aerospace components, housings, connectors, jigs and fixtures, short-run molds, and more.
Desktop Metal has just launched the ETEC Pro XL -- a premium polymer digital light processing (DLP) printer that enters the market at less than half the price as its predecessor. DLP is regarded by many as a superior polymer 3D-printing technology for speed, surface finish, and accuracy. Ideal for automotive and machine parts, aerospace components, housings, connectors, jigs and fixtures, short-run molds, and more.
Read the full article.
CNC machining case study: One-of-a-kind computer chassis
 Learn how Josh Sniffen, the YouTuber behind the popular PC-building channel "Not From Concentrate," trusted Xometry to provide a wide range of manufacturing options, personalized Design for Manufacturing (DFM) feedback, and order management support for his latest creation: the HEXO ATX computer chassis. All in all, Sniffen procured parts using Xometry's CNC machining service, selective laser sintering 3D-printing service, and sheet metal cutting and fabrication services. A neat insider look at the process.
Learn how Josh Sniffen, the YouTuber behind the popular PC-building channel "Not From Concentrate," trusted Xometry to provide a wide range of manufacturing options, personalized Design for Manufacturing (DFM) feedback, and order management support for his latest creation: the HEXO ATX computer chassis. All in all, Sniffen procured parts using Xometry's CNC machining service, selective laser sintering 3D-printing service, and sheet metal cutting and fabrication services. A neat insider look at the process.
Read this Xometry case study.
Which parts should be 3D printed? AI combs through CAD files to find out
 One of the biggest challenges in transitioning to additive manufacturing (AM) is the ability to identify which parts are best suited for the process quickly and easily. Learn how Danfoss, Stanley Engineered Fastening, and even the U.S. military have utilized advanced additive manufacturing software to automate the process, reducing material waste and energy costs, improving part reliability, decreasing lead times, as well as now having the ability to identify part consolidation opportunities through intelligent AM decision-making.
One of the biggest challenges in transitioning to additive manufacturing (AM) is the ability to identify which parts are best suited for the process quickly and easily. Learn how Danfoss, Stanley Engineered Fastening, and even the U.S. military have utilized advanced additive manufacturing software to automate the process, reducing material waste and energy costs, improving part reliability, decreasing lead times, as well as now having the ability to identify part consolidation opportunities through intelligent AM decision-making.
Read the full article.
9 key design tips for injection molding
 Keep costs down and quality up all while optimizing your injection molded designs with these helpful tips from Xometry. Learn how to build better injection molded parts and products -- using draft angles, ribs and gussets, radii, fillets, and more -- and set expectations for the injection molding process. Good info here.
Keep costs down and quality up all while optimizing your injection molded designs with these helpful tips from Xometry. Learn how to build better injection molded parts and products -- using draft angles, ribs and gussets, radii, fillets, and more -- and set expectations for the injection molding process. Good info here.
View the video.
Metal additive manufacturing: Rocket turbopump design
 Mixing undergraduate curiosity and real-world engagement, two students from Colorado University Boulder Aerospace Engineering Sciences program, Zachary Lesan and Patrick Watson, started an independent effort on turbopump design and manufacture that is a lesson in determination and industry collaboration. With lots of supplies and advice from industry heavy hitters including Velo3D, CFturbo, SpaceX, and many more, their project has reinforced significant points being made about next-generation rocketry.
Mixing undergraduate curiosity and real-world engagement, two students from Colorado University Boulder Aerospace Engineering Sciences program, Zachary Lesan and Patrick Watson, started an independent effort on turbopump design and manufacture that is a lesson in determination and industry collaboration. With lots of supplies and advice from industry heavy hitters including Velo3D, CFturbo, SpaceX, and many more, their project has reinforced significant points being made about next-generation rocketry.
Read the full article.
Transparent ceramics for extreme optics
 Sapphire is an inherently transparent ceramic material that is resistant to extremes of temperature and environment. Sapphire can be processed to unique and precise shape/form by diamond grinding and polishing to allow full transparency. INSACO is a global leader in this capability -- and working with ultra-hard materials in general.
Sapphire is an inherently transparent ceramic material that is resistant to extremes of temperature and environment. Sapphire can be processed to unique and precise shape/form by diamond grinding and polishing to allow full transparency. INSACO is a global leader in this capability -- and working with ultra-hard materials in general.
Learn more.
Heat-resistant camouflage makeup aims to shield Soldiers from bomb blasts
Camouflage face makeup for warfare is undergoing one of the most fundamental changes in thousands of years, as scientists recently described a new face paint that both hides Soldiers from the enemy and shields their faces from the searing heat of bomb blasts. Firefighters also could benefit from the new heat-resistant makeup, according to the report.

Image courtesy: Robert Lochhead]
It was part of a broader symposium on innovations in ingredients for personal care products held in August during the 244th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society, the world's largest scientific society. The meeting included almost 8,600 reports on new discoveries in science and other topics.
Robert Lochhead, Ph.D., who presented the report, explained that Soldiers have used face paint for centuries for one kind of protection to help their skin blend in with the natural environment and shield them from enemies. The new material continues that tradition, but also provides protection from the searing heat of roadside bomb blasts and other explosions that have claimed a terrible toll in Iraq, Afghanistan, and other conflicts.
Video caption: Heat-reflective camouflage makeup made by Bob Lochhead and a team from the University of Southern Mississippi keeps the left-hand strip at below 100°C after 10 sec under a blowtorch, whereas the unprotected strip reaches 400°C.
"The detonation of a roadside bomb or any other powerful explosive produces two dangerous blasts," Lochhead said. "First comes a blast wave of high pressure that spreads out at supersonic speeds and can cause devastating internal injuries. A thermal blast follows almost instantaneously. It is a wave of heat that exceeds 1,112°F. That's as hot as a burning cigarette. The thermal blast lasts only two seconds, but it can literally cook the face, hands and other exposed skin."
In an effort to protect soldiers from this threat, the U.S. Department of Defense has been seeking a solution that Lochhead initially regarded as an impossibility: A material that Soldiers could smear on their faces like suntan lotion, leaving a coating that although thinner than a sheet of paper, could protect against that intense heat. Dr. Paige Buchanan, Kelli Booth, Michelle McClusky, Laura Anderson, and Lochhead were the team that tackled the challenge. Not only did they succeed, but they discovered a formulation that protects in laboratory experiments way beyond the 2-sec heat-wave threat from improvised explosive devices and other bombs.
The new camouflage makeup protects the face and hands for up to 15 sec before its own temperature rises to the point where a first-degree burn, which is a mild burn, might occur. In some tests, the new face paint can protect for up to 60 sec, which could be important in giving Soldiers time to move away from blast-related fires and also for use by civilian firefighters.
The makeup had to meet several key criteria: It had to reflect intense heat; have camouflage colors suitable for day and night use; be easy to apply and remove; be waterproof; and be non-irritating to the eyes, nose, and mouth.
The trickiest part was that the University of Southern Mississippi team had to avoid the use of mineral oil, mineral spirits, fatty substances, and other traditional hydrocarbon makeup ingredients. Hydrocarbons can burn in contact with intense heat in the flame spectrum. The team turned to silicones, which are not as flammable because they absorb radiation at wavelengths outside of the intense heat spectrum. Silicones have been replacing hydrocarbons in many commercial cosmetic makeup products as cosmetics companies improve products to confer better feel properties and transfer resistance.
Another challenge was adding DEET, an insect repellent. The military mandates that all camouflage makeups contain 35% DEET. "DEET also is flammable, so when the Department of Defense asked us to incorporate it, we didn't think we could do it," Lochhead said. But the team successfully included DEET by encapsulating it in a hydrogel substance, a water-rich material that prevented DEET from catching fire.
It already has passed the preliminary laboratory tests needed to determine whether development should continue. Lochhead's team also plans tests of the material on other surfaces to try to protect clothing, tents, and other items from burning, and a colorless version is being developed for firefighters.
Source: ACS
Published September 2012
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
